(Research Assistant) Soft-Growing Robot Navigation in Unknown Environment via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Navigation Strategy for Soft-Growing Robots Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Brief Review
Soft-growing robots are an emerging field in robotics, offering significant potential for various applications. One critical aspect of their functionality is effective obstacle avoidance, especially in scenarios where the robots must navigate through narrow and intricate spaces. However, controlling these robots presents substantial challenges. The increasing degrees of freedom (DOF) associated with the growing number of segments complicate control strategies. Traditional control methods often fall short, as they struggle to manage numerous segments and require internal sensor integration, adding further complexity.
Project Summary
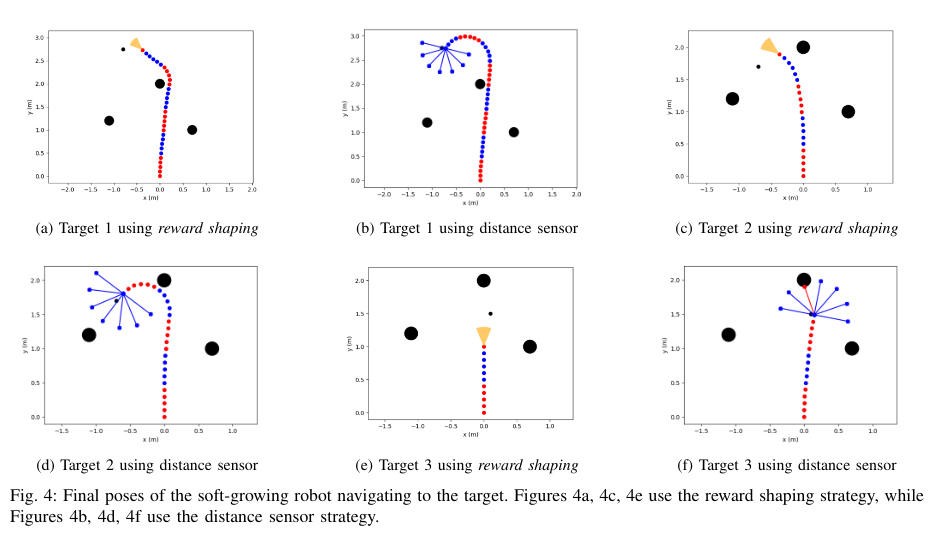
This research proposes a navigation strategy for a soft-growing robot using deep reinforcement learning in an unknown 2D environment consisting of simple obstacles. By employing two navigation strategies—reward shaping and distance sensors—the robot successfully avoided obstacles in 100 trials.
Key Contributions:
- Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach:
- Utilized deep reinforcement learning to handle the high DOF without the need for complex internal sensors.
- Enabled the robot to learn optimal navigation policies through interaction with the environment.
- Navigation Strategies:
- Reward Shaping: Adjusted the reward function to encourage the robot to reach the target while penalizing collisions with obstacles.
- Distance Sensors Reward: Implemented external sensing to provide real-time feedback, aiding in obstacle detection and avoidance.
- Performance Evaluation:
- Conducted 100 trials to assess the effectiveness of both navigation strategies.
- Results:
- Using Distance Sensors Reward: The robot reached its target with an average error of 0.36 ± 0.22 meters.
- Only Reward Shaping: Achieved an average error of 0.37 ± 0.27 meters.
Conclusion
The study demonstrates that deep reinforcement learning can effectively address the control challenges of soft-growing robots in obstacle-rich environments. By leveraging reward shaping and distance sensors, the proposed navigation strategies enable the robot to navigate successfully without relying on complex internal sensor integration. The results indicate that the robot can reach its target with minimal error, showcasing the potential for deploying soft-growing robots in applications requiring navigation through constrained and intricate spaces.
